Industrial chillers are essential for maintaining precise temperature control in manufacturing, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and large-scale HVAC systems. By removing heat from a process or space, they ensure equipment efficiency, product quality, and energy savings. In this guide, we’ll explore how industrial chillers work, their types, applications, and why they’re vital to modern industries.
What is an Industrial Chiller?
An industrial chiller is a cooling system designed to remove heat from a liquid via a vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycle. This chilled liquid can then be circulated through heat exchangers to cool machinery, industrial processes, or large commercial spaces.
How Do Industrial Chillers Work?
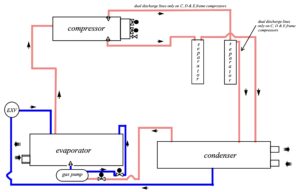
The working principle of an industrial chiller follows the basic refrigeration cycle:
- Evaporator – The refrigerant absorbs heat from the process water, cooling it down.
- Compressor – The refrigerant vapor is compressed, raising its pressure and temperature.
- Condenser – Heat from the refrigerant is released into the air or cooling water, turning the vapor back into liquid.
- Expansion Valve – The refrigerant pressure is reduced, lowering its temperature before re-entering the evaporator.
This continuous cycle maintains stable cooling for industrial operations.
Types of Industrial Chillers
- Air-Cooled Chillers – Use ambient air to dissipate heat. Ideal for outdoor installations with sufficient ventilation.
- Water-Cooled Chillers – Use cooling towers and water circulation. Suitable for larger facilities needing higher efficiency.
- Absorption Chillers – Use heat sources (like steam or hot water) instead of mechanical compression, often used where waste heat is available.
Applications of Industrial Chillers
Industrial chillers are widely used in:
- Plastic Industry – Cooling injection molding and extrusion equipment.
- Food & Beverage – Preserving product quality during processing and storage.
- Pharmaceuticals – Maintaining strict temperature control in production.
- HVAC – Cooling large commercial buildings and factories.
- Data Centers – Ensuring servers remain at optimal operating temperatures.
Benefits of Industrial Chillers
- Energy Efficiency – Reduces energy waste by optimizing heat removal.
- Equipment Longevity – Prevents overheating and mechanical failures.
- Consistent Product Quality – Maintains stable conditions during production.
- Environmental Sustainability – Modern chillers use eco-friendly refrigerants and energy-saving technologies.
Choosing the Right Industrial Chiller
When selecting a chiller, consider: – Cooling capacity (tons or kW) – Installation environment (indoor vs outdoor) – Operating costs and efficiency ratings – Maintenance requirements – Type of refrigerant and sustainability standards
Conclusion
Industrial chillers are the backbone of modern industries where precise temperature control is essential. Choosing the right chiller not only improves productivity but also saves energy and reduces operational costs. Whether air-cooled, water-cooled, or absorption-based, the right solution will depend on your specific industry needs.


